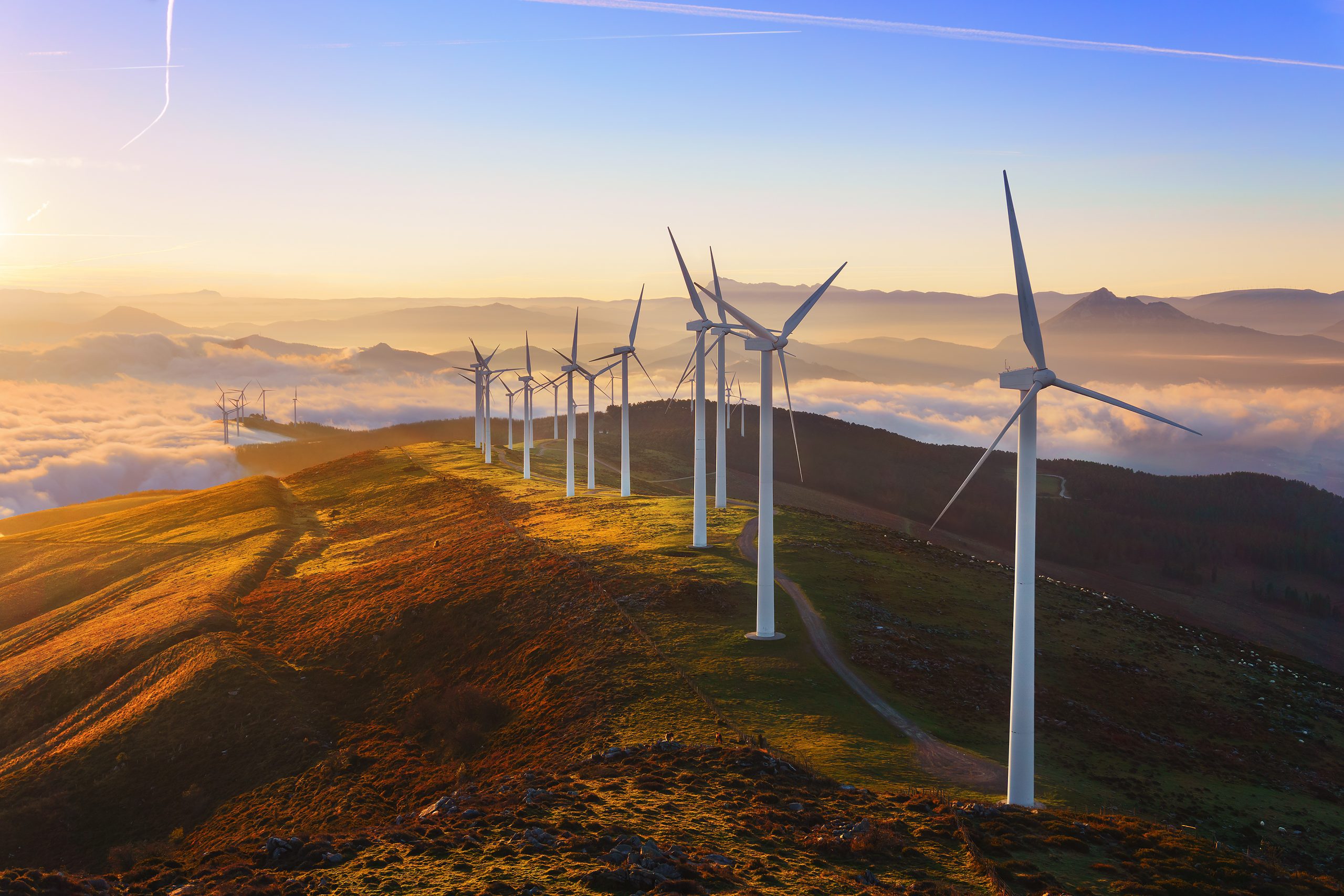
In recent years, the transition to renewable energy has become a central focus for nations across the globe. This movement is driven by the urgent need to address climate change, reduce carbon emissions, and meet the growing energy demands of modern societies. As we explore the progress and challenges of this transition, it becomes clear that while significant strides have been made, many hurdles remain.
Progress in Renewable Energy Adoption
Global Achievements
In 2024, a notable milestone was achieved when renewable energy accounted for 30% of global electricity production, a substantial increase from less than 19% two decades ago. This growth has been largely driven by solar energy, which, despite representing only 6% of the global energy mix, has experienced a 20% annual growth rate in recent years.
Key Highlights
- Solar energy is the fastest-growing renewable source.
- Electricity demand is expected to soar (in large part thanks to AI and the expansion of data centres).
- The announcement during the last COP was to triple the financial goals (for climate-related financing to USD 300 billion).
- Per the last World Economic Forum report, 107 of the 120 benchmarked countries have shown progress toward a shift to alternative energy.
Regional Insights
Each region has its unique landscape and contributions to the global energy transition:
USA
- Continued growth in renewable energy projects, particularly solar energy.
- Despite progress, several challenges impede the transition:
Financial Obstacles:
- High inflation and interest rates increase project costs.
- Supply chain disruptions lead to delays and cancellations.
Non-Cost Barriers:
- Opposition: “Not In My Backyard” sentiment opposes large-scale projects due to land use concerns.
- A backlog in transmission line installations hampers grid connectivity. Capacity would need to double or triple to meet expected demand.
Latin America:
- Brazil leads with 85% reliance on renewables, primarily hydroelectric power.
- Chile and Brazil have emerged as regional leaders in renewable energy development.
- Growth is expected in solar and wind projects, particularly in Chile and Mexico.
Asia-Pacific:
- Over 52% of global power generation is attributed to this region, with China playing a pivotal role.
- China accounts for nearly 36% of global solar generation, although nationally, only 6% of its electricity mix is solar power.
- China leads the world in wind energy, boasting a wind turbine capacity of 441,895 megawatts—nearly three times that of the U.S., which ranks second. A 340-meter-tall 26MW wind turbine has been built in 2024, with a wingspan of 12 Boeing 747s for comparison purposes.
- China has reduced coal’s share in its energy mix from 61% to 52% in just one year. However, China still has a coal power capacity of 1,125 GW that is not committed to any further closure. Compared to only 123 GW of coal power capacity retired since 2000, China is still heavily reliant on coal power.
- Renewable energy in 2030 is expected to make up 30% to 50% of the power generation mix in most APAC markets, with renewables playing a dominant role in mainland China, Laos, and Vietnam.
Europe:
- Wind and solar energy have overtaken coal and gas in electricity generation with Germany, the UK and Spain being the top contributors to this shift away from fossil fuels
- The region aims for a 55% reduction in GHG emissions compared to 1990 levels by 2030, with significant progress achieved in emissions reduction.
Regulatory Challenges:
- Strict power purchase agreements in Asia restrict flexibility in transitioning to renewables.
- Delays in policy decisions and lengthy approval processes deter investment in renewable projects.
- Many countries still rely on state-owned utilities, which complicates direct deals between renewable energy producers and consumers
- Carbon leakage, which is where emitters move production to less-regulated areas, remains a challenge for Europe
Social Challenges:
- Expansion of wind and solar projects in Southeast Asia has raised concerns among local communities regarding land use and environmental degradation.
- Companies often lack adequate engagement with affected communities, resulting in social tensions on protected areas.
Vulnerability to Natural Disasters / CAT events
- Southeast Asia is already facing significant climate-related challenges, including increased frequency and intensity of extreme weather events such as heat waves, floods, and tropical cyclones. These events threaten energy infrastructure, particularly solar and wind facilities, which can be severely impacted by heavy rainfall and high winds.
Phasing out Fossil Fuels
- Premature retirement of coal plants causes a significant loss of profits for investors, which have invested billions of dollars with the expectation of generating returns for the entire duration.
- Easier said than done – investors would need to be provided with a sufficiently adequate incentive before they agree to shut down the coal plants early, and these incentives currently are rare to none.
The Merit Order and Electricity Pricing
The Merit Order is a principle used to set electricity prices by ranking available sources in ascending order of their marginal cost to produce electricity. As renewable energy sources like wind and solar become more prevalent, they lower the overall cost of electricity but also increase price volatility due to their intermittent nature.
“With the increase in renewables, the challenge is balancing supply and demand while managing market pricing.”
The Role of AI and Renewables in Energy Markets
Artificial intelligence (AI) is poised to revolutionize energy markets by optimizing efficiency and integrating renewables more effectively. While AI is often seen as a consumer of energy, innovations such as AI-designed wind turbines demonstrate its potential to enhance energy efficiency.
Conclusion
The global transition to sustainable power generation has made commendable progress, yet significant challenges remain. As we continue to move forward, the focus must be on overcoming these obstacles through innovative solutions, robust infrastructure development, and supportive regulatory frameworks. The journey is complex, but with concerted effort and collaboration, a sustainable energy future is within reach.
“The path to renewable energy is fraught with challenges, but through innovation and persistence, we can achieve a sustainable future.”